Rainwater Runoff Control Measures
In recent years, there has been a trend of increasing localized heavy rainfall across the country, raising the risk of flooding due to rainwater. To protect the lives and property of citizens and maintain urban functions, the city is promoting measures to control rainwater runoff along with the development of public sewerage for rainwater.
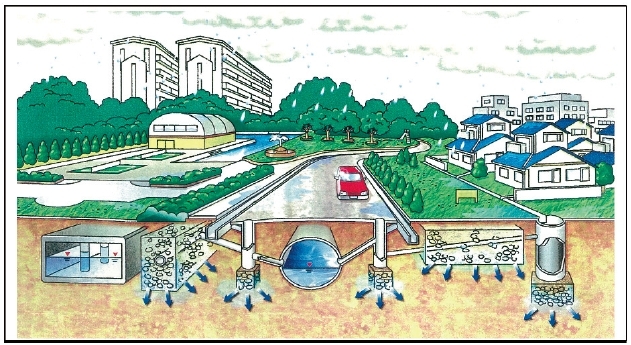
To control the runoff of rainwater, we are working in collaboration with relevant departments to preserve permeable areas such as green spaces and parks. Rainwater drainage facilities (such as rainwater pipes) are large-scale and require significant costs and time for development. Additionally, due to the need to respond to localized heavy rainfall in recent years, we are promoting the installation of not only rainwater drainage facilities but also rainwater infiltration facilities and rainwater storage facilities.
Rainwater Infiltration Facility
This is a facility for efficiently allowing rainwater to permeate into the ground. Examples include rainwater infiltration pits and infiltration trenches.
By allowing rainwater to permeate underground, it becomes groundwater and can be effectively utilized as a healthy water circulation resource.
Rainwater infiltration pit
Rain that falls on the roof is directed to the rainwater infiltration basin through gutters and other means.
A rainwater infiltration basin with a diameter of 25 centimeters has the capacity to infiltrate approximately one bathtub's worth of rainwater into the ground per hour.
Rainwater infiltration tanks allow rainwater to permeate through the holes in the bottom and sides, as shown in the photo below.


Infiltration Trench
In addition to rainwater infiltration basins, further infiltration effects can be achieved by installing infiltration trenches.
Although it cannot be seen in daily life, it can be constructed on the premises as shown in the photo below. Rainwater permeates through the perforated pipe and the gravel at the bottom.

Rainwater Storage Facility
This is a facility for temporarily storing rainwater to utilize it as a water resource or to delay the outflow of rainwater. Examples include storage tanks and retention basins.
Retention Tank
This is a facility that collects rainwater that falls on building roofs and other surfaces.
By installing a storage tank, rainwater can be temporarily stored and used as valuable domestic water for home gardens, watering trees, and during disasters.
Retention Basin
A facility for temporarily storing rainwater from the entire watershed, which delays the outflow of rainwater to the downstream area, aiming to cut the peak outflow and reduce flooding damage.

Please let us know your feedback on how to make our website better.
Inquiries about this page
Inagi City Urban Environment Management Department Sewerage Division
2111 Higashi-Naganuma, Inagi City, Tokyo 206-8601
Phone number: 042-378-2111 Fax number: 042-378-9719
Contact Us for the Sewerage Division, Urban Environment Management Department, Inagi City